Cannabidiol (CBD) oil is a natural plant extract that’s gained popularity in recent years for its numerous health benefits. CBD oil is extracted from the hemp plant using different methods, including cold pressing and CO2 extraction.
What Is Cold Press CBD Oil?
Cold press CBD oil is a natural extract that’s obtained using cold press extraction method. This process involves crushing the hemp plant’s seeds, stems, and leaves to extract the oil. Cold press extraction method primarily uses hydraulic pressure, resulting in minimal heat exposure during the extraction process.
What Is CO2 Extraction CBD Oil?
CO2 extraction is a popular method of obtaining high-quality CBD oil. This process involves using pressurized carbon dioxide (CO2) to extract the oil from the hemp plant’s seeds, stems, and leaves. CO2 extraction typically involves a series of steps, including pressurized CO2 exposure, separation and filtration to obtain purified CBD oil as the final product.
The 4 Differences Between Cold Press CBD Oil and CO2 Extraction CBD Oil
- Efficiency: CO2 extraction is a more efficient method for extracting CBD oil as it produces a higher yield of CBD oil per batch compared to the cold press method.
- Purity: CO2 extraction method produces a cleaner and more pure CBD oil free of contaminants compared to the cold press method.
- Cost: Cold press CBD oil is relatively cheaper compared to CO2 extraction CBD oil.
- Terpene Profile: Cold press CBD oil typically retains the natural terpenes present in the hemp plant, giving it a unique flavor and aroma. On the other hand, CO2 extraction CBD oil may not retain the terpene profile of the hemp plant, thus lacking the natural flavor and aroma.
Which One is Better: Cold Press or CO2 Extraction?
When it comes to choosing between cold press CBD oil and CO2 extraction CBD oil, the choice ultimately depends on individual preferences and needs. Here are some considerations to keep in mind when choosing between these two extraction methods:
- Specific Uses: Cold press CBD oil is better for consumers who want to use the oil for its flavor and aroma properties. CO2 extraction CBD oil, on the other hand, is better suited for consumers who prioritize purity and efficiency.
- Cost: For consumers looking to save on costs, cold press CBD oil is a more affordable option, whereas CO2 extraction CBD oil is more expensive but also more potent and effective.
- Extraction Type: If the hemp plant’s terpene profile is important, then cold press extraction may be the better choice, while if purity and efficiency are a higher priority, CO2 extraction is the better method.
Conclusion
While both cold press and CO2 extraction methods have their merits, the choice ultimately depends on the user’s individual preferences and needs. Cold press CBD oil offers a more affordable, natural, and flavorful option for those who prioritize terpene profiles. On the other hand, CO2 extraction CBD oil provides a more pure and potent product for those who prioritize purification and efficiency. In the end, it is the user’s preferences, budget, and specific needs that will determine which method is the better one.
Further reading: Extraction Methods for Cannabidiol
What is Cannabidiol?
Cannabidiol, abbreviated as CBD, a type of cannabinoid, is the main chemical component in industrial cannabis, extracted from female cannabis plants.
How does CO2 extraction work?
Carbon dioxide extraction uses pressurized CO2 as a solvent to draw desirable compounds from cannabis, the actual process is relatively straightforward.
There are two basic steps in the CBD carbon dioxide extraction method.
First, the ground cannabis solids are placed in the extraction chamber. Pressurized carbon dioxide is pumped into the chamber where it dissolves the plant material and separates compounds such as cannabinoids.
In the second step, a pressure release valve facilitates the release of the material into a separate vessel, where heat and pressure encourage the cannabis compounds to separate from the carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is then exposed to a different temperature and pressure. This enables it to restabilize as gas and flow back into the CO2 tank, leaving behind amber-colored cannabis oil.
Cold press vs co2 extraction CBD
CO2 has been designated generally accepted as safe (GRAS) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Carbon dioxide is the most common compound used in high-pressure extraction. It boasts a number of benefits compared to other solvents used for botanical extraction.
For starters, carbon dioxide is a non-toxic substance that is readily available commercially for lower costs than other chemical alternatives. In addition, carbon dioxide is environmentally safe, and straightforward to work with, and it creates a superior product typically free of any by-products or residue. Modification of the temperature and pressure allows different cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds to be targeted, allowing the extraction process to be customized for different formulations. Most importantly, the nature of the CO2 extraction process itself tends to result in a superior product.
CO2 extraction vs cold press
Cold Press extraction is most commonly used in the production of essential oils, but some CBD brands tout it as their extraction method. The technique is typically reserved for fruits like citrus contained in the skin. Therefore, it cannot be used effectively to extract CBD from Cannabis. Any CBD brands that state they have used cold press are actually unlikely to have any CBD in their CBD Oils.
Cold press methods produce less total oil per batch than CO2 extraction.
CO2 extracts can vary – depending on the plant material and extraction conditions – between macerated extracts, pressed oils, or essential oils. Their high price is compensated for by the high quality, longer shelf life, and lower application dosage compared with conventional oils, extracts, or essential oils.
Two attributes
- The first feature of Cannabidiol is not addictive, and it has pharmacological effects such as antispasmodic, anti-anxiety, and anti-inflammatory.
- The second characteristic is that it can also eliminate the hallucinogenic effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on the human body, known as anti-drug compounds.
These two attributes determine the CBD’s greatest value for industrial cannabis.
Chemical nature
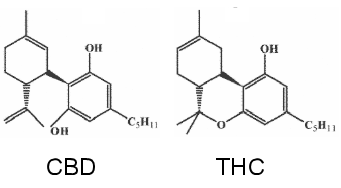
The CBD was originally an organic compound isolated from Indian cannabis by Adams and Todd in 1940. In 1963 Mechoulam and Shvo measured their chemical structure. The chemical formula of CBD is C21H30O2 with a molecular weight of 314.46 Daltons.
From the structural point of view, CBD has optical activity and cis-trans isomers, and the natural CBDs are all left-handed trans-structures, namely (-)-trans-CBD.
Under normal temperature and pressure, the CBD is white or pale yellow resin or crystal, melting point 66-67 ° C, boiling point 463.9 ° C (760 mmHg), density 1.025 g / cm3, almost insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents.
Because the chemical formula and molecular weight of CBD are completely consistent with THC, the physical and chemical properties of the two are very close, which leads to the difficulty in extracting CBD from industrial cannabis, which constitutes the technical barrier of the industry.
Extraction Methods
At present, the main methods for extracting active ingredients (usually organic compounds) from plants include steam distillation, pressing, and extraction.
Among them, the distillation method is suitable for substances with strong volatility, and the pressing method is suitable for the extraction of eschar materials that are liquid at normal temperatures. Since the CBD has a boiling point of more than 400 degrees at normal temperature and pressure and is insoluble in water, the extraction method is the most suitable extraction method.
After reviewing the current CBD extraction methods, we can summarize the CBD enrichment/extraction process into the following process, which is divided into four parts, including pre-treatment steps such as pulverization and drying, extraction steps, and concentration after extraction. A chromatographic purification step and a post-treatment step for the purified sample. Among them, extraction and purification are key steps.
- Solvent extraction: The main advantages of the organic solvent extraction method are simple operation, low requirements on equipment, and low energy consumption. The disadvantages are that the organic solvent is liable to remain, the solvent dissolving ability is constant, and environmental pollution may occur.
- CO2 extraction process: The main advantage of the supercritical carbon dioxide extraction method is that the separation range is wide, and the adjustment of the dissolution ability of the extractant can be achieved by changing the temperature and pressure, but the equipment requirements are high, the energy consumption is large, and the instrument cleaning is difficult.
At present, organic solvent extraction and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction are widely used, and subcritical water extraction is a new technology, which has not been used in the industrial production of CBD.
Organic solvent extraction
The organic solvent extraction method can also be divided into soaking extraction, reflux extraction, and ultrasonic extraction.
- Soaking extraction: Soaking extraction is to directly extract and mix the organic solvent and the material for extraction, which takes a long time.
- Reflux extraction: Reflux extraction is carried out by heating and distilling the leachate, distilling it and then condensing it, and then refluxing it back into the leather to continue the extraction process. Although the extraction efficiency is improved, continuous heating may cause the CBD. damage.
- Ultrasonic extraction: Ultrasonic extraction is a method that uses ultrasonic mechanical effects, cavitation effects, and thermal effects to improve extraction efficiency. Ultrasonic extraction can be carried out at a lower temperature, and the extraction speed is fast, the efficiency is high, and the solvent usage is small, which has certain advantages over the former two.
CO2 extraction
The traditional carbon dioxide supercritical extraction uses pure carbon dioxide gas to reach a critical state under a certain temperature and pressure, showing the characteristics of the fluid and extracting the material.
However, in practice, in order to improve the extraction efficiency, a mixed CO-solvent, called an entertainer, is usually added to the superfluid, which is the main direction of the development of the supercritical extraction method.
How Processing Hemp Helps Improve CBD Extraction Rates
The first step in the CBD extraction process is the selection of raw materials.
The content of CBD in the raw material has a direct influence on the yield and purity of the final extraction. The higher the content of CBD in the raw material, the higher the yield and purity under the same process conditions.
Similar to THC, the content of CBD in various parts of cannabis is usually decreased in the order of bracts, flowers, leaves, stalks, and thick stems, and is highest in flowers and leaves of female flowers. Therefore, the processing of the CBD is usually carried out using the leaves.
In the treatment of raw materials, drying and comminution steps are usually included. The water in the raw material is reduced to 8% or even 5% by heating or drying. The meshing number is usually about 50-200 mesh to increase the contact area with the extraction reagent during the extraction process and improve the extraction efficiency.
Enzymes
There are also companies that use cellulase, pectinase or complex enzymes after drying and pulverizing to destroy the cell wall of cannabis to further improve extraction efficiency. However, the addition of enzymes also increases production costs. From the perspective of industrial production, the addition of enzymes may require comprehensive consideration.
CBD concentration and chromatographic purification
CBD concentration
The extracted extract is usually concentrated by heating before being purified by a chromatography column, the extraction solvent is evaporated and removed, and an extract composed of components such as CBD is left.
The effect of evaporation and concentration can remove some volatile impurities on the one hand, and replace the solvent with the mobile phase required for chromatography, on the other hand, facilitating chromatographic purification.
The steps of replacing the solvent are more flexible, and the changes are different in different technologies. In some techniques, the method of water sedimentation is used for concentration, and in some techniques, the organic solvent is used for multiple dissolution and concentration.
Chromatographic purification
The extract is dissolved in a solvent using a chromatographic mobile phase and then purified by a column. Purification of the column is carried out based on the difference in properties such as molecular weight and polarity of the different components.
Commonly used column packings include silica gel, macroporous adsorption resin, polyamide adsorption resin, etc., each of which can be subdivided according to chemical composition or crosslinking. Chromatographic elution solvents often use polar or non-polar organic solvents.
Different chromatography columns and different solvents can remove different impurities, and the recovery rates are not the same. In some technologies, a variety of chromatographic columns are combined to purify to improve the purity.
However, in the chromatographic process, the purity is usually not compatible with the recovery rate.
The selection of the column, the choice of the chromatographic solvent, and the choice of the chromatographic purification method need to be comprehensively considered.
Post-purification treatment
The chromatographically purified CBD solution also needs to be concentrated to remove the solvent to obtain a higher purity CBD oil or ester. The crystal of the CBD or the CBD sesame oil is then prepared by evaporation, drying, or supersaturation.