Supercritical CO2 extraction is a widely used method for extracting useful compounds from natural sources, including astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pigment found in Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae. In this article, we will discuss the supercritical CO2 extraction of astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis, including the process, advantages, and applications.
The Extraction Process
The process of extracting astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae using supercritical CO2 involves prepping the starting material. The algae are harvested, washed and dried to produce the dried biomass. The dried biomass is then subjected to supercritical CO2 within an extraction vessel under high pressure and temperature. The CO2 is then allowed to disperse as the pressure is gradually reduced, leaving behind astaxanthin extract.
Advantages of Supercritical CO2 Extraction
- Supercritical CO2 extraction has several advantages over other extraction methods. Firstly, it is a clean and efficient process that does not require the use of harmful chemicals or solvents. Supercritical CO2 is non-toxic and can be recycled, making it environmentally friendly.
- Secondly, the SFE provides high selectivity since the supercritical CO2 can selectively extract targeted compounds. This results in a high yield of pure and concentrated astaxanthin extract.
- Thirdly, the SFE is a relatively easy and safe process that can prevent natural pigments from breaking down. Astaxanthin may break down under high temperatures, but the low temperatures used in the supercritical CO2 extraction process can prevent this.
Applications of Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pigment that has various therapeutic applications. It may protect against tissue damage, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce inflammation and oxidative damage in the body. Additionally, astaxanthin may improve exercise performance and skin health, and it is an essential component of several health supplements and cosmetic products.
Comparison with Other Extraction Methods
Other methods of extracting astaxanthin, such as solvent extraction and mechanical extraction, also produce high yields of astaxanthin. However, solvent extraction requires the use of harmful solvents, which can be problematic from an environmental and safety perspective. Mechanical extraction, on the other hand, is less efficient and cannot selectively extract astaxanthin.
Therefore, SFE represents a clean, efficient, selective, and low-temperature method of extracting astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae.
CO2 extraction process of astaxanthin
- Pulverization degree: 20-60 mesh
- Extraction pressure: 70 MPa
- Extraction temperature: 40°C
- Separation pressure I: 14 MPa
- Separation I temperature: 45°C
- Separation pressure II: 6 MPa
- Separation II temperature: 40°C
- Extraction time: 120 min
Where is astaxanthin extracted from?

The functional components contained in Haematococcus Pluvialis-the specific physicochemical properties of astaxanthin ester and free astaxanthin, the use of supersonic airflow (broken wall) crushing, supercritical CO2 extraction can be used to extract the Haematococcus Pluvialis The biologically active ingredients (astaxanthin) are effectively extracted, and then separated and purified by molecular steaming and other processes, and refined into “Haematococcus Pluvialis oil” and “Astaxanthin microcapsules”.
The CO2 extraction process of astaxanthin
The innovation of the supercritical CO2 extraction process.
This process is a special extraction process. Compared with the conventional supercritical CO2 extraction process, the process of this project has carried out the technical transformation of the supercritical CO2 extraction equipment and added a composite entrainer (edible alcohol).
Ethyl linoleate continuous addition equipment, using a high-pressure pump to feed at a constant speed, so that the fat-soluble components and alcohol-soluble components in Haematococcus Pluvialis can be extracted at one time under low temperature (35″C) conditions, Synchronously completed the work that the conventional process needs to be carried out in multiple steps, shortening the processing time from the traditional process (alcohol, ethyl acetate extraction process) from 3 days to 7 hours;
The astaxanthin content in the raffinate after extraction is less than 0.3%, and the astaxanthin content in the extract (Haematococcus Pluvialis oil extract) is greater than 5.0%
Haematococcus Pluvialis oil extract contains free astaxanthin with polarity. Through the reasonable selection of the solvent system, the difference in polarity between free astaxanthin and other substances in the extract is used to separate it from other substances.
In this process, a unique combination of solvent systems is selected: ethyl linoleate-ethanol. By optimizing the ratio, free astaxanthin can be effectively separated, and the astaxanthin extraction rate can reach 66.69%. The content of astaxanthin in algae oil extract can reach 5.71%
PRETREATMENT PROCESS
The storage of Haematococcus Pluvialis raw materials and the pretreatment process of supercritical CO2 extraction is studied.
The storage of Haematococcus Pluvialis raw materials needs to be stored in cold storage; before the supercritical CO2 extraction, the Haematococcus Pluvialis Silica powder needs to be added with silicon dioxide as an antagonist (the antagonist is removed during extraction) to improve the fluidity of the raw material during supersonic airflow (wall-breaking) pulverization and wall-breaking pulverization. Five different two types are used. Treat the raw materials with the amount of silica added, and then observe the effect on the fluidity of the raw materials.
It is found that when the amount of antagonist added is 8.0%, the fluidity of the raw materials is the optimization. After the wall is broken and crushed, the average Haematococcus Pluvialis powder is The particle size is 9.75ug; the particle size is: 500 mesh, the wall breaking rate is greater than 97.0%
Wet granulation. Use 12.0% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) solution as a binder; then use 70.0% ethanol/water as a wetting agent and select 3 main factors that affect the granulation process.” 2% HPMC slurry addition amount A, 7. The addition amount B of% ethanol and the mixing time C are used as the inspection factors, and the particle yield rate is used as the inspection index for the test.
Weighing and preparation
Add 12% HPMC slurry (500C heat preservation) to a stainless steel dish containing broken Haematococcus Pluvialis powder in the proportion designed in Table 1. After mixing well, add 70% ethanol and mix well for use.
Granulation
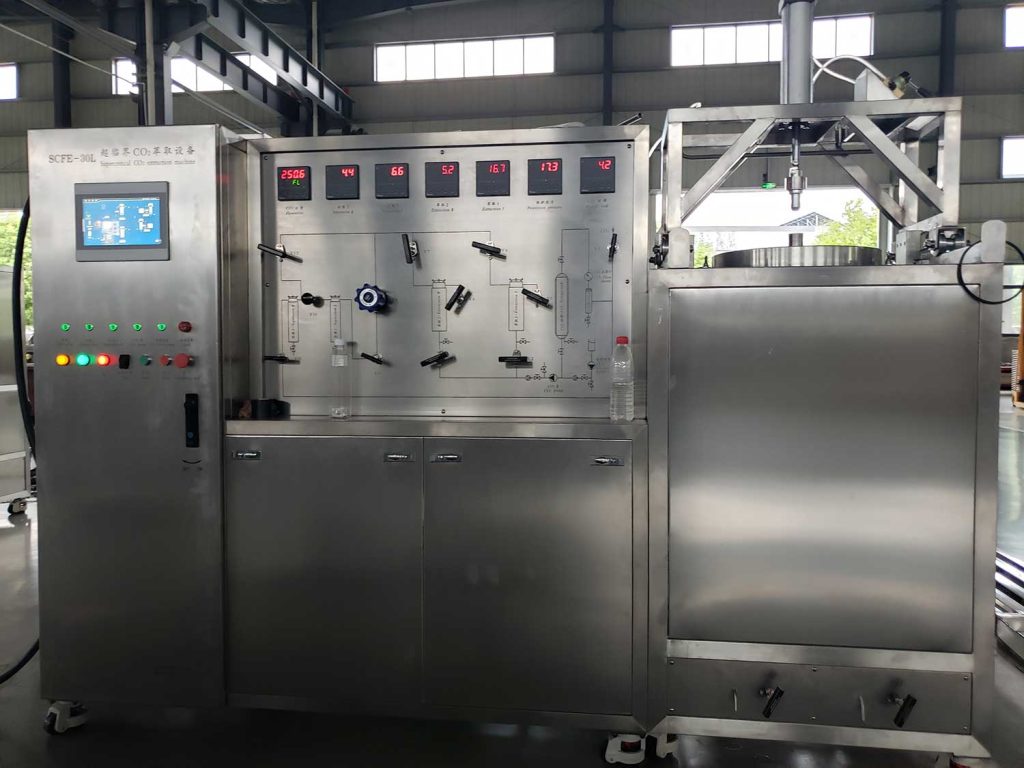

The uniformly mixed wet material is passed through a 12-mesh sieve, and the obtained particles are placed in a stainless steel plate and spread evenly; placed in a drying box at 50°C, dried for 3.5 hours, then sieved with a 40-mesh sieve, and the obtained particles are weighed and For fine powder, record the total weight M of the material after granulation and drying and the weight of the granule obtained by sieving m·
Get the optimization co2 extraction process
CO2 extraction pressure
The extraction pressure has the greatest impact on the experiment. When the temperature is constant, the pressure increases, and the density of supercritical CO2 also increases, thereby increasing the solubility of CO2. When the pressure increases to a certain level, the solubility of CO2 increases very slowly. We set the extraction experiment conditions as raw material particle size 20-40 mesh, extraction temperature 40°C, extraction time 2h, CO2 flow rate: 20~30L/h, separator I pressure 14MPa, separator I temperature 45°C, separator II pressure 6MPa, The temperature of separator II is 40°C, and the experimental results show that the optimal extraction pressure is 70MPa.
co2 extraction temperature
The extraction temperature is restricted by the stability of astaxanthin. The storage of astaxanthin requires low temperature, protection from light, and oxygen isolation. According to the characteristics of astaxanthin, we set the extraction experiment conditions as follows: raw material particle size 20-40 mesh, extraction pressure 70MPa, Extraction time 2h, CO2 flow rate: 20~30L/h, Separator I pressure 14MPa, Separator I temperature 45°C, Separator II pressure 6MPa, Separator II temperature 40°C, and the experimental results are shown in the table below.
The experimental results show that the optimal extraction temperature is 40°C.
extraction time
When the extraction pressure, temperature, flow rate, and other conditions are constant, the longer the extraction time, the higher the extraction yield. The CO2 extraction experiment conditions are set as follows: raw material particle size 20-40 mesh, extraction pressure 70MPa, extraction temperature 40°C, CO2flow rate: 20 ~30L/h, Separator I pressure is 14MPa, Separator I temperature is 45°C, Separator II pressure is 6MPa, Separator II temperature is 40°C.
particle size
The broken wall Haematococcus Pluvialis powder is made into three different particle sizes for the CO2 extraction machine;
The particle size was 10-20 mesh; 20-40 mesh*40-60 mesh 丨 Compare the effect of the particle size of Haematococcus Pluvialis on the extraction yield. The supercritical CO2 extraction process conditions are extraction pressure 70MPa, extraction temperature 40C, extraction time 7 hours, and CO2 flow rate: 2O~3OL/h.
The experimental results show that the particle size of 20-40 mesh is the optimization particle size.
CO2 flow rate
If the flow rate of CO2 is too low, the extraction time will be prolonged; if the flow rate is too high, the CO2 will leave without reaching saturation with the raw materials in the circulation, resulting in waste of CO? and other resources. Therefore, the flow rate generally adopts empirical values, according to our Experience, the flow rate of CO2 is 20~30L/h.
Conclusion and analysis
The optimization process conditions obtained in this experiment are: raw material particle size 20-40 mesh; extraction pressure 30MPa, extraction temperature 40°C; extraction time 2h, CO2 flow rate: 20-30L/h, separator I pressure 14MPa; separator I temperature 45 °C The pressure of separator II is 6MPa; the temperature of separator II is 40°C, the feeding amount of each batch is 10kg of Haematococcus Pluvialis particles, and the amount of entrainer is 60kg per batch
This process can effectively extract astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis particles so that the average content of total astaxanthin in the raffinate (residue) is 0.224%, and the extract yield (based on oil extract) Total amount) can reach 28.5%, and the extraction rate of astaxanthin can reach 66.69%
Due to the lack of light-shielding conditions in the experiment, the stability of astaxanthin is poor after being extracted. In the subsequent preparation process, astaxanthin has a large loss. It is necessary to improve the light-shielding conditions to further increase the astaxanthin. The extraction rate.
Astaxanthin has a wide range of applications in food, medicine, chemical, cosmetics, and other industries. The research and development of its new technology is a work of important strategic significance, and it plays a guiding role in the industrialization of Haematococcus Pluvialis.
Summary
In this experiment, Haematococcus Pluvialis spore powder produced by Yunnan Aier Bio-Technology Company was used as raw material. After supersonic airflow (breaking the wall), pulverization, granulation, and drying were used to prepare Haematococcus Pluvialis spore particles (particle shrimp The content of penicillin is 2.44%); the experimental conditions are set as follows;
Raw material particle size 20-400, extraction pressure 70MPa, extraction temperature 40°C, extraction time 2h, CO2 flow rate: 20~30L/h, separator I pressure 14MPa, separator I temperature 45°C separator II pressure 6MPa, separator II The temperature is 40°C.
The dosage of each batch is 10kg of Haematococcus Pluvialis pellets, and the dosage of each batch of entrainer is 60kg•
After filtering each batch of extracts, use a rotary vacuum thin-film evaporator to evaporate the ethanol under the conditions of 50C and a vacuum of -0.08MPa. The resulting extract (oil extract) is used to determine the total astaxanthin content by spectrophotometry. content.
Conclusion
Supercritical CO2 extraction is an effective method for the extraction of astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae. The extraction process is environmentally friendly, highly selective and efficient, and ensures preservation of the natural properties of the pigment.
Astaxanthin is a multi-functional health supplement with broad therapeutic applications. It is commonly used in cosmetic products, dietary supplements, and functional foods.
By using a comparison table and advantages list, this article has presented a clear and concise format that showcases the benefits of supercritical CO2 extraction over other extraction methods. Overall, supercritical CO2 extraction is a technical choice for companies seeking to produce high-quality astaxanthin, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly method of extraction.
Advantages of Supercritical CO2 Extraction:
- Clean and environmentally friendly
- Selective and efficient
- Low-temperature extraction
Comparison of Different Astaxanthin Extraction Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| SFE | Clean, efficient, selective, environmentally friendly, low-temperature, and does not require the use of harmful chemicals | Requires equipment |
| Solvent extraction | High yield | Uses harmful solvents |
| Mechanical extraction | N/A | Less efficient and cannot selectively extract astaxanthin |
Overall, supercritical CO2 extraction is a technical choice for companies seeking to produce high-quality astaxanthin, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly method of extraction. The extraction process is highly selective and efficient, ensuring the preservation of the natural properties of the pigment, and by utilizing a list and a comparison table, this article highlights the benefits of this extraction method over other methods. With its various therapeutic applications and broad use in the cosmetics and food industry, astaxanthin offers an array of unique benefits to human health and well-being.